IAB Video Ad Standards: A Comprehensive Guide
Reading Time: 7 minutesDigital video is exploding in popularity. The convergence of technology advancements and consumer behavior adjustments has resulted in the present video landscape’s expansion. With the rate at which the digital advertising industry is growing, it requires regulation to ensure that numerous parties can work in harmony. However, adhering to the IAB Video Ad Standards enables publishers and advertisers to more effectively manage their video ad on various platforms like TV, mobile, desktops, tablets, laptops, etc.

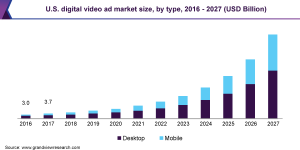
It’s no secret that video advertising is expanding in the United States, accounting for a sizable portion of total media spending in the country. According to eMarketer’s analysis, this trend is predicted to continue through 2023, when total expenditure on digital video advertising in the United States is expected to reach $58.39 billion.
The Growth of Video Advertising
Two key reasons marketers and publishers find the process of selling and distributing video advertisements complex are the following:
- Inadequate understanding of the technological capabilities of video players.
- Consumption of video advertisements across numerous screens, such as televisions, laptops, and mobile devices.
Although the majority of video advertisements are viewed on PCs, their consumption on mobile devices and smart TVs has exploded in the last decade.
Due to the fact that video advertising is more engaging and interactive with users, it leaves a lasting impression, making it one of the most popular advertising forms. This has resulted in a rise in US digital advertising expenditure on video from $152.71 billion in 2020 to $239.99 billion in 2021. Additionally, these figures are expected to surpass $300 billion by 2025.
What are IAB Video Ad Standards?
The Interactive Advertising Bureau (IAB) is a global organization charged with defining technical standards for advertisers, publishers, and other ad tech sector partners in order to assure consistent growth. For marketers and publishers, the IAB created a variety of video advertising standards for a variety of platforms (desktop, mobile app, mobile web, etc.). These technical specifications define video advertising standards and associated metrics such as ad size, delivery method, file format, and aspect ratio. The IAB’s guidelines are intended to streamline the advertising industry and enable players to operate cooperatively.
Video ad standards are mainly for publishers, video ad developers, and ad tech vendors.
- Publishers: They can use these video ad standards to transcode the file to the appropriate format for the intended audience.
- Video ad developers: The advertising guidelines for video advertisement developers include ad space, maximum file size, CPU load, and other metric criteria.
- Advertisers and ad servers: For them, these standards to define video ad metrics such as bounce rate, impressions, page value, overall site traffic, cost per thousand impressions (CPM), clicks, quality score, and conversions.
The most popular video ad standards of IAB are:
- VAST (Video Ad Serving Template)
- VPAID (Video Player Ad-serving Interface Definition)
- VMAP (Video Multiple Ad Playlist)
VAST – Video Ad Serving Template
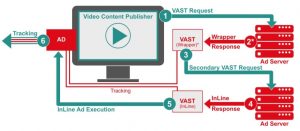
The Video Ad Serving Template is an XML-based template that ensures a consistent delivery format for in-stream video advertisements across a variety of streaming video platforms, including tablets, mobile devices, and desktop computers. To be more specific, VAST elevates the video advertising ecosystem by establishing a common interface between video players and ad servers that enables seamless video ad display. It was developed in 2008 to assist publishers, ad-tech providers, and ad networks, and has been modified numerous times since then to reflect evolving trends.
Capabilities of VAST:
- Creates scripts that deliver advertisements to video players.
- Sends metadata regarding the ad’s delivery method.
- The server distributes the VAST file to a video player together with click-through URLs, creative files, and reporting trackers, among other things.
- Provide instructions to video players on how to handle advertisements, including their display, duration, and skippability.
- Specifies methods for quantifying video in terms of impressions, clicks, and tracking points.
- Allow publishers and media companies to set the pricing of video inventory based on the cost-per-completed-view (CPCV).
Evolution of VAST:
- 2008-VAST 1.0: It was an initial specification that standardized video advertisement responses to describe a video ad.
- 2009-VAST 2.0: This IAB video ad standard added support for various ad formats (linear, non-linear, and over-lays) and conversational media files.
- 2012-VAST 3.0: Added support for skippable ads, in-ad privacy notices, ad pods, and better tracking events and error codes.
- 2016-VAST 4.0: It featured Mezzanine file support to enable Server Side Ad Insertion; introduced viewability support and explicit verification; separated media files from verification and interactive code.
The VAST 4.1 standard was announced in 2018 and the VAST 4.2 in 2019.
VPAID – Video Player Ad Interface Development
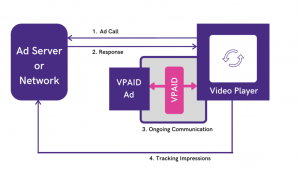
Image source
The IAB’s video advertising standards for Video Player Ad Interface Development serve as a standardized interface for ad units and ad players to provide an interactive advertising experience. Additionally, VPAID records ad playback and user interaction.
The IAB intends to use VPAID to address the following market inefficiencies affecting advertising, publishers, and vendors:
- Provide marketers with standardized technical criteria in order to reduce the cost of creative production and enhance ROI.
- Increase in the availability of common video advertisements to enable publishers to accept video advertisements served by ad servers.
- Increase the liquidity of the video ad supply by lowering the cost of integration.
Capabilities of VPAID:
- It enables rich interactivity and defines a set of APIs that enable the ad to recognize the video ad.
- VPAID permits the collecting of extensive data on human-computer interaction.
- It enables publishers to specify delay tolerances.
- This IAB standard enables video advertisements to tell the video player on how to handle mistakes and timeouts.
- It enables marketers to implement any logic they desire, including cookie deletion, viewability measurement, and ad serving logic.
Evolution of VPAID:
- VPAID 1.0 (2009): This section provides the APIs used to communicate between ad units and video players in order to create interactive video experiences.
- VPAID 2.0 (2012): It included support for JavaScript creatives and a slew of changes to enhance interactive experiences.
VMAP – Video Multiple Ad Playlist
Similar to VAST, VMAP or Video Several Ad Playlist is an XML template that enables the placement of multiple ad slots within video ad content when the video player or distribution channel for the video content is not controlled. This IAB standard enables the owner of video content to exercise control over ad inventory in order to maximize revenue while maintaining the integrity of their program’s content.
IAB Video Ad Standards –Digital Video Ad Formats
The IAB had divided digital video advertising into two distinct video ad formats – Linear and Non-Linear – while maintaining a common set of video ad standards.
- Linear video ads: Linear video adverts, like television commercials, produce an interruption in the streaming video content. They can be played prior to, during, or following the streaming material.
- Non-linear video ads: These advertisements are pictures that appear on top of streaming video content. In this video ad type, the advertisement runs concurrently with the streaming material, and the user may view the advertisement without being distracted from the streaming content. Nonlinear advertisements can be presented in the form of static images, text, video overlays, or interactive rich media.
- Companion ads: These video advertisements are accompanied by linear and nonlinear advertisements in the form of display advertisements, static advertisements, text, rich media, or a skin wrapped around the film. Companion advertisements come in a range of sizes and designs.
IAB Video Ad Standards: Linear ad format standards
The following linear ad format standards outline the bare minimum requirements for developing linear ads.
- Insertion point: It can be put prior to, during, or following the roll.
- Duration of maximum ad display: For linear ad formats, the maximum ad duration is 6 seconds, 15 seconds, or 30 seconds.
- Click event: Both the video window and accompanying advertisement may contain links to the advertiser’s website.
- Controls: Prior to the campaign’s launch, controls such as fast forward, skip the ad, and so on should be negotiated.
- Dimensions: The optimum aspect ratio is 16:9, but 4:3 is acceptable.
IAB Video Ad Standards: Non-linear ad format
Find below the non-linear ad format standards and the minimum requirements for ad development.
- Insertion point: It can be placed during the play of a video advertisement.
- Duration of maximum ad display: For linear ad formats, the maximum ad duration is 5-15 seconds or persistent.
- Click event: When users click on overlays, they expand to interactive advertisements, auto-played videos, or the advertiser’s website.
- Controls: A persistent close button in the ad unit’s upper right corner must enable viewers to quit at any time.
- Dimensions: The ad’s initial dimensions can be 300*50 or 450*50. The overlay cannot exceed 1/5 of the player’s height. Publishers may, however, grant an additional 20 pixels for flying sparks or drop shadows.
- Label: The ad unit should be labeled as an “Advertisement” either within the ad frame or adjacent to it.
- Opacity: The text and image must be completely opaque, while the backdrop should be 70% opaque.
- Maximum file size: The file size for the initial portion of the advertisement is 100k.
Final Thoughts
As per the recent update in the IAB video ad standards, the anticipated growth in popularity of Connected Television (CTV) over the last few years prompted the IAB Technology Laboratory to recently announce an update to the Digital In-Stream Video and CTV Ad Formats guidelines for 2022. Unprecedented expansion in the use of CTV products in the video ad landscape, along with new technological breakthroughs, has prompted this technical standards-setting body for digital advertising to revise the IAB Video Ad Standards. The most recent requirements discuss the resolution, file size, colour space, and bitrate for TV ratios and popular players, as well as the production of several files to aid in intelligent creative selection during programmatic cross-screen insertion.
VDO.AI is a leading innovative video ad solutions service provider that ensures to follow all standards related to digital video advertising while providing services to the advertisers and publishers.



